Heat is defined as the heat energy
possessed by a substance. In general, to detect the presence of heat possessed
by an object by measuring the temperature of the object. If the temperature is
high, the heat contained by the object is very large, and vice versa if the
temperature is low, the heat contained slightly.
From the experimental results are
often conducted heat required size of an object (substance) depends on three
factors:
1. Mass of
matter
2. Type of
substance (specific heat)
3. Temperature
changes
When two or more thermal contact occurs there will be a flow
of heat from higher temperature object to a lower temperature object, to
achieve thermal equilibrium. This heat transfer process takes place within
three mechanisms, namely: conduction, convection and radiation.
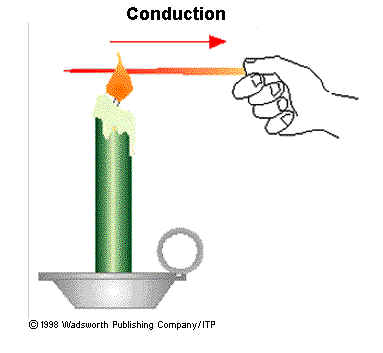
a. Conduction
If a metal is
heated in one end tertenu time interval, the other end will feel the heat. This
shows that the metal rod that flow or heat transfer occurs from the
high-temperature metal to metal parts of a low temperature. Heat transfer in
metal that do not follow the mass transfer is called heat transfer by
conduction. So is the conduction heat transfer through an intermediary and
agent for the heat transfer occurs, it is not accompanied by the displacement of
particles of intermediary substances.
Heat transfer
in solids can be explained by atomic theory. Atoms in solids are heated to
vibrate strongly. A vibrating atoms will move some of its energy to the nearest
neighbor atoms pounded. Then the neighboring atoms are crushed and get this
heat will come and strike neighboring atoms vibrate more, so on so that heat
transfer occurs in solids.
Terms of heat
conduction of a body is the temperature difference between the two places on
the object. Heat will move from place to place at high temperature low
temperature. If the temperature of both places being the same, then the
propagation of heat also be stalled.
Based on the
ability of a substance dissipates heat conduction, the substances can be
classified into two categories, namely conductors and insulators. Conductors
are substances that can conduct heat well, while the insulator is the opposite,
ie substances that are difficult to conduct heat. From the experimental results
obtained that the heat transfer by conduction depends on the type of metal,
cross-sectional area conductor of heat, the temperature difference between the
ends of the metal, as well as the length of the conductor through which the
heat is.
b. Convection
At the time of
heating water on the stove using a saucepan, heat propagation will occur from
the water in the bottom of the pan to the surface by convection. Based on
observation, as this heat transfer occurs in a substance that flows, as in
liquids and gases. Convection heat transfer in different heat transfer in
conduction, convection, where the incident occurred a mass movement or the
movement of particles of intermediate particles, whereas the conduction events,
this does not happen. The move took place because they kind of mass differences.
Due to the heat, the density of the substance at the bottom (which is closer to
the heat source) will be reduced, so that will be lighter than the substance in
it. This light causes the substance to move upward, while the heavier
substances will move downward. So forth, so that the water in the pan will
continue to go up and down spins.
From this
convection problem will be obtained that the propagation of heat by convection
depends on the thermal convection coefficient of heat transfer substance, the
heat transfer surface area, as well as the temperature difference between the
heat flow with heat dumps.
Convection can happen to:
1.
Liquids
Terms of the solid liquid convection
is the heating. This is due to the particles involved move liquids.
2.
Gases
Convection occurs also in the gas,
for example air. As with the water, propagation (flow) heat the gas (air)
occurs by convection. Some of the events that occurred as a result of air
convection is as follows.
ü
The
existence of the sea breeze. Sea breezes occur during the day. During the day,
land gets hot faster than the sea so that the air in the land rises and is
replaced by air from the ocean.
ü
The
existence of onshore wind, onshore wind occurs at night. At night, the land to
cool faster than the oceans. Thus, the air over the ocean rises and is replaced
by air from the mainland.
ü
The air
circulation in the room at home and the presence of the factory chimneys.
b.
Radiation
Radiation
is heat
transfer in the form of
electromagnetic waves. In radiation, heat or
energy propagates
without the need for an
intermediary substance,
unlike the case with conduction or convection is always
in need of a medium.
Virtually every
object emits and absorbs radiation energy. There are glowing hot
objects, and some are not
glowing. The
second object is
dispersive / radiate heat energy in
the form of electromagnetic
waves with
different wavelengths.
Joseph
Stefan finds
that the rate
of propagation of heat by radiation per unit
area of
surface will
depend on the nature
and temperature
of the object
surface. Shiny objects disperse heat more difficult than
things that
dull. This
situation also
applies to objects
that absorb
heat. Glossy surface objects more difficult
to absorb
heat than a
black body
and dull the surface. So
it can be said
that black and
dull object
is a radio transmitter and a
good heat
absorbed.
Effect of heat on an object other than to increase the temperature of an object
can result in changes in states of matter. Material change is the change
properties of a substance or material into another substance either into a new
substance or not. A
material usually experience changes in temperature when heat transfer occurs
between the materials with their environment. In a given situation, this heat
flow does not change its temperature. This occurs when the phase change
material. Eg solid to liquid (melting), liquid to vapor (boiling) and changes
in crystal structure (solid). The energy required is called heat or latent heat
of transformation.
All around us there are a variety of objects such as water, metal, wood. Alcohol, the air we breathe, or helium gas used to fill helium gas.
These objects be grouped into three states of matter, namely:
1. Solids, for example iron and wood
2. Liquid, for example water and alcohol
3. Gas, for example heliun and oxygen
Joseph Stefan finds that the rate of propagation of heat by radiation per unit area of surface will depend on the nature and temperature of the object surface. Shiny objects disperse heat more difficult than things that black and dull. This situation also applies to objects that absorb heat. Glossy surface objects more difficult to absorb heat than a black body and dull the surface. So it can be said that black and dull object is a radio transmitter and a good heat absorber.
Such items are subject to change shape. based on changes nature of the substance changes form the substance can be classified:
1. Merged: Changes in the form of solids to liquid
2. Freeze: Change a liquid form into solids
3. Yawning: Changes in liquid form into a gas
4. Condense: Changes in the form of gas into a liquid substance
5. Sublimes: Change in solid form into a gas
6. Deposed: Changes in gas form into solids
Material change are divided into two kind:
a. Changes in physic
Changes in physics is a process of change in physical appearance of an object with a basic identity unchanged. These changes are temporary and do not produce new substances. For example rice into rice flour.
b. Chemical changes
A chemical change is a material change in circumstances include not only physical, but also the identity of the base. These changes can also occur simultaneously in an event, such as candles are lit, some wax melted and then froze again, some candles burning to gas. Chemical changes are permanent and produce new substances. Material changes chemically accompanied by:
1. Discoloration
2. The occurrence of sediment
3. The emergence of gas
4. The occurrence of heat.
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed Twitter
Twitter 4/15/2014
4/15/2014
 Unknown
Unknown



 Posted in
Posted in 

0 komentar:
Posting Komentar